2D SDS PAGE analysis of purified Drug Substance (DS) samples provides an orthogonal method of confirming HCP removal during processing steps. The analysis steps are similar to those used for testing HCP antibodies on whole cell lysates. Samples are loaded on duplicate 2D silver-stained gels and on duplicate 2D gels to be transferred to PVDF for western blotting. One of the western blots is probed with the anti-HCP antibody. The duplicate western blot is probed with an antibody against the DS, since the sample contains a large amount of DS this helps determine which proteins are DS and which are HCP. When determining the HCP antibody coverage, the DS spots are omitted from the analysis.
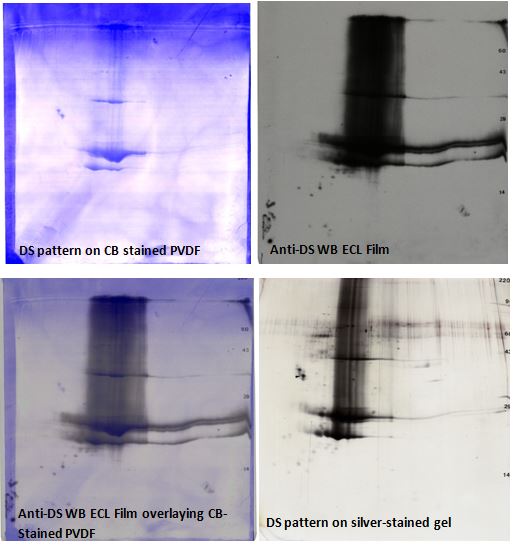 Figure 1. Anti-DS 2D western blot images. Upper Left: Coomassie blue-stained PVDF, Upper Right: anti-DS ECL Western blot film, Lower Left: Western blot overlay image; and Lower Right: silver-stained 2D gel pattern. Spots reacting to the DS ab are omitted from the analysis. Heavily loaded DS samples sometimes show vertical trailing, breakdown products, and polymers as seen here.
Figure 1. Anti-DS 2D western blot images. Upper Left: Coomassie blue-stained PVDF, Upper Right: anti-DS ECL Western blot film, Lower Left: Western blot overlay image; and Lower Right: silver-stained 2D gel pattern. Spots reacting to the DS ab are omitted from the analysis. Heavily loaded DS samples sometimes show vertical trailing, breakdown products, and polymers as seen here.
Film images are warped to the silver-stained 2D gel with TotalLab SameSpots software using the Coomassie blue-stained PVDF membrane image (before western blotting) to facilitate alignment. Spots detected by the anti-DS ab are omitted from the analysis along with any buffer blank spots. The remaining spots detected by silver-staining and the anti-HCP ab are outlined to determine the anti-HCP ab coverage. Spots visible only with the anti-HCP ab but not detectable by silver staining are added to the analysis as indicated by small blue dots on the silver-stained gel.
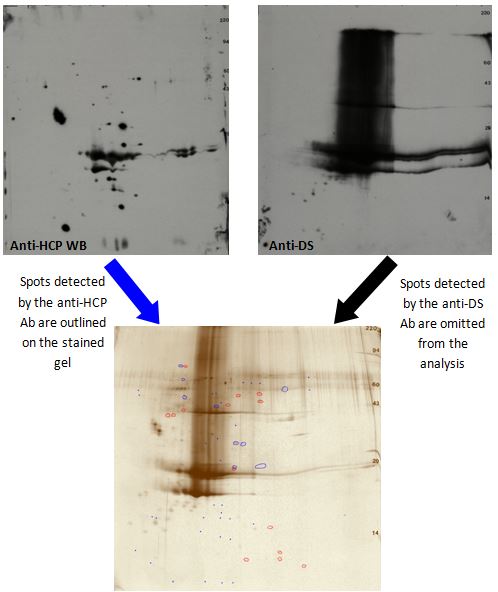
This method can be used to monitor the removal of HCPs during the DS purification process. It is also useful to confirm removal of most HCPs from the final DS. Finally, in combination with duplicate Coomassie blue-stained 2D gels, HCPs can be further analyzed using mass spectrometry.
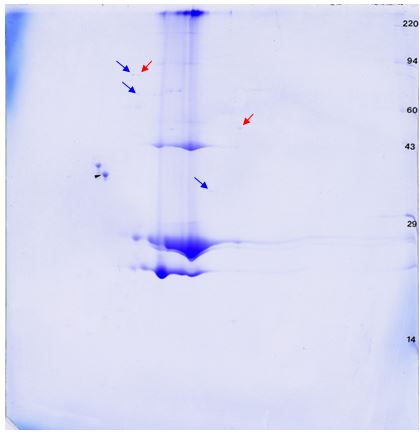
Identification of protein spots of interest by mass spectrometry would give additional supporting information. Spots not detected by the HCP antibody or DS antibody could be DS breakdown products, DS multimers, or HCP not detected by the ab. Determining the identity of HCP proteins (either detected or not by the HCP ab) allows for assessment of importance of their removal from the final DS and informs strategies for modification of the purification process for removal of remaining HCPs.